The Open Metaverse

Written by George Agathangelou
The metaverse, one of the most hyped terms of 2022, is still in its infancy but it has garnered unprecedented levels of attention on some of the world’s top media platforms. Even though many trust that the metaverse constitutes the most important paradigm shift for the net, the metaverse is genuinely a misunderstood concept, mainly due to the fact that strictly speaking, it has not been developed fully yet. In this blog post, we will try to demystify the terms surrounding this phenomenon and highlight the importance of an Open Metaverse.
Notwithstanding that existential disadvantage, the Metaverse has managed to attract several of the most popular manufacturers and organizations, which include Sotheby’s, Nike, Adidas, Gucci, the NFL, McDonald’s, and even banks including J.P. Morgan, and engage them in buying digital land NFTs to set up shop in the metaverse. If you would like to explore all the known use cases of NFTs, then check this blog out.

These brands are setting up shops within the virtual world, to drop limited collections, mint NFTs and auction off million-dollar digital artworks. The metaverse also became the hottest concert venue with performances by artists such as Ariana Grande, Justin Bieber and Lil Nas X, all in avatar format.
Ok, so now that we have your attention, let us start with some definitions to supply a bit of context.
Metaverse refers to the concept of a highly immersive virtual world where people gather to socialize, play, and work. The Metaverse is the virtual alternative to our physical universe and maybe the next version of the internet. NFTs potential in the Metaverse reinvents the ways assets can be bought, sold, or traded without real-world constraints such as raw resource limits or supply chain risks.
Web3 is a new concept of the Internet that not only implements storage, exchange, and semantic search of any content but also provides a truly decentralized interaction of independent counterparties of any activity with no control or censorship.
NFT (non-fungible tokens) are digital representations of data, that embed digital authenticity and ownership and support the creation of intangible assets. NFTs are essentially composable digital objects that fundamentally create unique opportunities and connections to off-chain analogues and will support all metaverse assets and transform the class of intangible assets to a new class of assets.
In case you are looking for more definitions, make sure to check our Glossary.

Speaking of definitions, here is Gartner’s definition of the metaverse:
“The metaverse is a persistent and immersive digital environment of independent, yet interconnected networks that will use yet-to-be-determined protocols for communications. It enables persistent, decentralized, collaborative, interoperable digital content that intersects with the physical world’s real-time, spatially oriented and indexed content. Access is currently device-dependent and includes experiences spanning the immersive (augmented, mixed, and virtual reality) spectrum”.
Today it is impossible to imagine the Internet without social networks. But back in 1992, it was in principle difficult for many people to imagine what the Internet itself was. Neal Stevenson, however, was not one of those people. Even the founding fathers of cyberpunk, William Gibson and Bruce Sterling, admitted that the author of “Snow Crash” is much more versed in all things information technology than they are.
The metaverse described in the novel is in many ways like a social network: people socialize, exchange any type of files, “consume” information or distribute it. The only significant difference is that the Metaverse allows you to fully immerse yourself in the virtual world.
In the Metaverse, you can gather with friends instead of going to a bar, cafe, or cinema, in your own house. In addition, entertainment in the Metaverse is more spectacular and interesting than the real world can offer. But it is also a place for work, meetings, negotiations. In fact, any meeting that takes place on Zoom today in the world of “Snow Crash” would take place in the Metaverse, in a building that belongs to your company, and the conference room would not differ much from the real one. So, Metaverse could be something that can potentially replace today’s Internet as it brings the digital experience into the real world and vice versa.
Facebook — Meta’s closed silo and their Metaverse
I recently managed to get hold of an Oculus Quest 2 and was eager to try the immersive experience through this generally regarded best-value-for-money headset. I was not very surprised to see that I could only set up the device by logging on to Facebook under the prying eyes of Meta Corp. However, there is still hope for privacy advocates as there is a way to create an Oculus account without a Facebook account, by downloading a 3rd-party Android application and hacking the device(Here is a guide for Android users, sad news for Apple users).
Nonetheless, after a while, I was able to navigate Meta’s “metaverse” which is nothing but a closed-circuit environment and had no way of interacting with web3 applications. Heck, I couldn’t even download and install my favorite web browser and extensions such as Metamask. Nonetheless, the quality of the handset and accessories, the free apps included and a journey in the Multiverse brought about many smiles and good times, among myself and my associates testing out VR for the first time.
(Here is a photo of Block.co’s CEO playing a shooting game on Oculus during lunch break!)

I am also hoping that there will be ways to open up the device to popular applications and services outside of Meta’s closed environment in the near future and that Meta will consider shifting its business model to a hardware manufacturer instead of data merchant.
In 2021, the CEOs of Microsoft, Epic Games and Facebook simultaneously spoke about the development of their metaverse. And each company sees the image of the virtual universe of the future in its own way.
The idealistic metaverse according to Ball will appear only decades later as this requires simultaneous development in many IT areas. It can be thought of as a “successor” to the mobile Internet. Users will have devices and platforms through which they interact with the metaverse. Its emergence may be based on a stack of eight major strands in technology and thinking, writes Ball. In July 2021, he compiled a “textbook on the metaverse” detailing the development of each direction.
As Matthew Ball stated:
“We need to think of the Metaverse as a sort of successor state to the mobile internet. And while consumers will have core devices and platforms through which they interact with the Metaverse, the Metaverse depends on so much more. There’s a reason we don’t say Facebook or Google is the internet. They are destinations and ecosystems on or in the internet, each accessible via a browser or smartphone that can also access the vast rest of the internet. Similarly, Fortnite and Roblox feel like the Metaverse because they embody so many technologies and trends into a single experience that, like the iPhone, is tangible and feels different from everything that came before. But they do not constitute the Metaverse.”
Facebook has already invested heavily in virtual reality, spending $2 billion to acquire VR developer Oculus. Zuckerberg acknowledged that current VR headsets are “a little clunky” and need to be improved so people can work with them all day long. According to him, Facebook/Meta is working on a metaverse that will allow you to physically feel the presence of other people through space. It will be designed for virtual reality headsets, AR (augmented reality), PC, mobile devices, and gaming consoles.
Meta is also testing the first VR remote app, Horizon Workrooms, where Oculus Quest 2 headset users can meet as avatars. The official release is scheduled for 2022. VR headsets have already received the updates necessary to fully work in the application.
So, the Metaverse must be interoperable and cross-platform, whether in software or hardware, because otherwise, it will not be possible to create the scale necessary to cover the entire Internet.
Ok so far, but how is Blockchain-related to Metaverse?
Many new platforms powered by blockchain technology use NFTs and cryptocurrencies to create, own and monetize innovative decentralized assets.
Now, Blockchain technology promotes the virtual world and is strongly connected to the Metaverse. Blockchain technology has contributed to creating a fantastic virtual space where both users and businesses can benefit. Cryptocurrencies and NFTs make it possible for users to buy and sell these virtual assets online without making any physical contact. People try to speculate from it, and some enjoy minting their art as an NFT. In some cases, people are using NFT as a form of ticket for virtual events. Blockchain technologies have been utilized for various things, including buying virtual land, creating NFTs, and many more, and all these blockchain technologies are creating a metaverse that can be experienced as an evolution on the Internet.
So, without blockchain technology, the Metaverse would be incomplete as everything would be stored on a centralized network. The Metaverse is not similar to what the Internet offers today. Blockchain Metaverse offers proof of existence to every digital item by connecting through individual nodes worldwide. For example, Decentraland is an Ethereum-based 3D virtual world, where users can play, interact and explore and play games with each other. Decentraland allows its users to login through a web3 wallet address in order to buy virtual lands, build their own surroundings and applications and exchange digital assets on its marketplace.
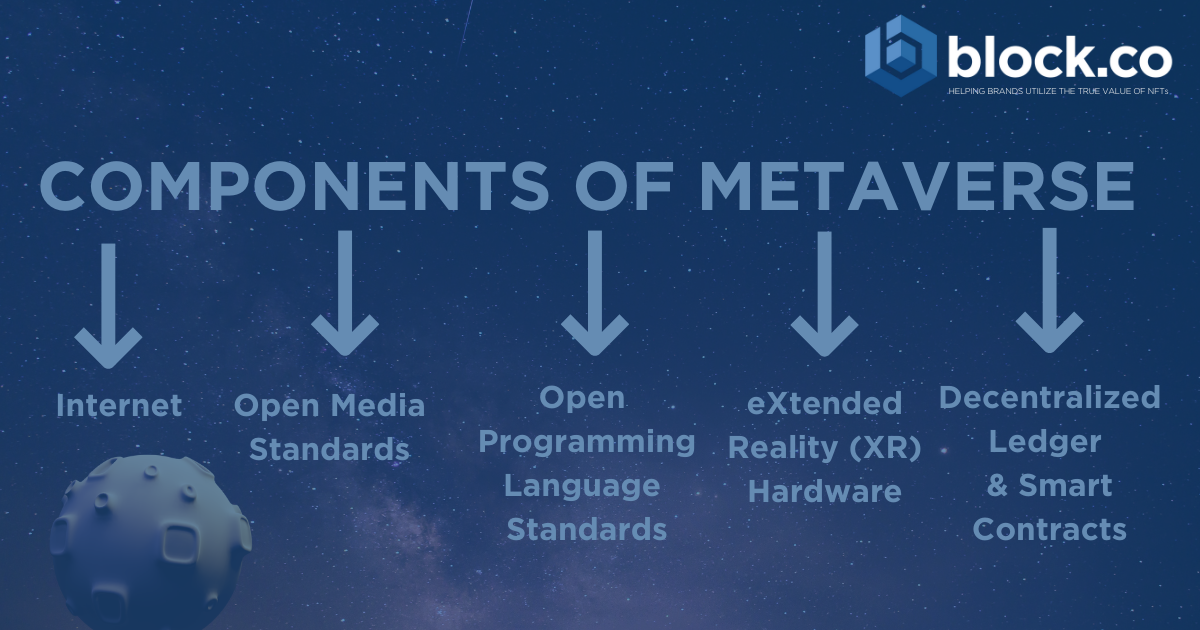
Components of Metaverse
Let’s now define the fundamental components that make up the Metaverse, which is a digital world in which anything can exist.
The following parts must work in perfect compatibility to establish the thriving metaverse:
Internet
Internet is a decentralized network of computers that is not owned by any individual organization or government and does not require any such organization’s centralized permission to use.
Open Media Standards
Standards are required to ensure cross-platform interoperability of audio, video, images, text, 3D scenes, vectors, etc. Pixar USD and NVIDIA MDL are big steps towards interoperability for 3D applications.
Open Programming Language Standards
Open programming language standards are required to govern any of the above to create applications in the metaverse. Such standards include HTML, JavaScript, WebAssembly, WebXR, WebGPU, Shading Language, etc.
eXtended Reality (XR) Hardware
For decades, virtual reality and augmented reality have been the main terms used in academia and industry, but in recent years additional terms have become popular. For example, eXtended Reality (XR) was created to describe the full range of possibilities of virtual (VR) and augmented (AR) reality and has become a convenient universal tool for many forms of immersive media. Thus, the ability of these technologies to expand the boundaries of the physical space-time continuum due to the capabilities of digital tools for working with human perception is emphasized. Immersive solutions based on VR / AR and several assistive technologies are today one of the most promising areas of XR in the practice of many industries.
Blockchain, Smart Contracts & NFTs in the Metaverse
Decentralized ledgers and smart contract platforms are the final components of the design of a blockchain metaverse. Blockchain networks are crucial as they help to sustain and guarantee better transparency and censorship resistance, permissionless in transactions.
Ethereum, Theta, Bitcoin, Binance Smart Chain (BSC) and others are the most famous examples of blockchain platforms used for the metaverse. They provide a significant base for the ownership economy that can in turn help in boosting the metaverse.
A smart contract is a contract with the terms of agreement between parties being directly written into code. The code and the terms of the contract contained therein exist across a distributed, decentralized blockchain network. The lines of code enforce the execution while transactions are traceable, transparent and irreversible. Without the need for a central authority or a legal system or an external enforcement mechanism, smart contracts allow trusted transactions and agreements to be performed.
The 3 key features of blockchain-built metaverses evolve around decentralization, user governance and real-world value.
The early virtual worlds were owned and absolutely managed via centralized entities. On the other hand, blockchain metaverses tend to be decentralized with a few or all of their operations backed by blockchain. The architecture of blockchain games can open up more fair engagement possibilities for all players which also means that ownership of the metaverse space is shared equally across its user base. When it comes to user governance, games such as Decentraland, make use of DAOs. DAO stands for “Decentralized Autonomous Organization”. The Decentraland DAO owns the most important smart contracts and assets that make up Decentraland — the LAND Contract, the Estates Contract, Wearables, Content Servers and the Marketplace. It also owns a substantial purse of MANA which allows it to be truly autonomous as well as subsidize various operations and initiatives throughout Decentraland. In this way, the metaverse environment can in turn become much more than just a simple crypto game as it can potentially turn into an entire society led by its own economic and leadership models. So, if we are to assume that the metaverse is a parallel augmented representation of the real world, it could also be the notion of an extension of it. And in an analogous manner to what occurs with ownership contracts within the actual world, NFTs allow holders to own their belongings and put them to good use, whether it is a valuable Cryptopunk or Bored Ape avatar, a plot of digital real estate or an in-game item within the metaverse environment.

Talking about DAOs, the recently launched ApeCoin ($APE) that was provided as a reward to BAYC NFT holders was not developed by Yuga Labs, the founders of the BAYC. Instead, it was founded by ApeCoin DAO in a display of decentralization. However, ApeCoin will also be used by Yuga Labs as the primary token for all new products and services such as the anticipated game associated with BAYC and the Benji Bananas game developed by Animoca.
According to the co-founder of Reddit and board member of the Apecoin DAO, Alexis Ohanian:
“Today we’re making the ‘Club’ bigger with ApeCoin… Web3 is being integrated into our art, music, and culture more and more every day and it all starts with community. I believe this community will build, expand, partner, and disrupt in a massive way.”
We trust that NFTs and the metaverse will stay rather analogous of their future development and could most likely keep on growing hand in hand. That is in the end due to the fact that NFT-based metaverses which incorporate digital assets and blockchain into their underlying era can bring in a wholly new financial framework and a modern economic paradigm within their respective ecosystems. In fact, while metaverse-like environments have existed in large multiplayer online games for some time now, the implementation of blockchain, NFTs, virtual belongings and virtual reality within the zone is not only significantly changing who can take part in and enter these environments, but also proving the actual-world marketplace price of the assets, the interactions and the reviews earned within the virtual realm of blockchain video games.
A new study by Wunderman Thompson (WPP), a New York-based global marketing communications agency, showed that 93% of global consumers agree that technology is our future. Metaverse may become one of the main technologies of the near future. In fact, humanity creates a separate new world that will eternally change the way we communicate, socialize and shop.
Gen Z consumers have grown up with social media and e-commerce and are increasingly expecting brands to serve their specific needs. They also know that they have the tools to publicly criticize the company in case of negative interactions, and the ability to easily switch to competitors who are easy to find online and have digitally transformed to adapt to the Metaverse.
TL;DR the time is NOW to get positioned in the Metaverse. The virtual economy will become as important as the physical economy. Vlad Panchenko, CEO and Founder of DMarket, a marketplace and technology for building virtual worlds stated in Forbes:
“Many brands intuitively or on purpose are moving towards the metaverse which is creating a global economy on track to exceed the current one many times over. There will be no other option but to join it. Otherwise, you will not survive as a company.”
The metaverse isn’t a single product one company can build alone. Just like the internet, the metaverse will exist with or without you! And with this opportunity to be a pioneer and enter the “empty space” and new ways to interact with consumers, also lies great responsibility. Responsibility to build an Open Metaverse, a Metaverse that sees no centralized silos of tech giants, enables interoperability, improves lives, builds equality, and creates connections for everyone, not just the wealthy and well connected.
For example, Gartner provides recommendations for technology innovation leaders as follows:
· Develop digital business strategies that leverage the built-in infrastructure and participants of the Metaverse.
· Lead idea and innovation management that focuses on new opportunities and business models with the Metaverse.
· Identify the unique technology risk, privacy and security implications in this new persistent and decentralized environment.
· List the outcomes, opportunities and obstacles the Metaverse entails in the form of an emerging-technology wheel.
To this end, the University of Nicosia, to which Block.co is a spinoff company, has established the Open Metaverse Initiative, a new comprehensive initiative focused on the academic, research and policy issues relating to the metaverse, with a particular emphasis on open public systems and standards.
If your brand is ready to take the step into web 3.0 and NFT marketing, to optimize engagement with your audience in innovative ways, then click the button below to get your Free Trial, a limited number of Free NFTs, and a Free Consultation call from our team!
Contact Block.co directly or email at enquiries@block.co.
Tel +357 70007828
Get the latest from Block.co, like and follow us on social media:
Sources:
https://medium.com/@sheetz.e/the-internet-is-cool-but-have-you-heard-of-the-metaverse-d3adf6ee57b3
https://medium.com/centrality/everything-you-need-to-know-about-the-open-metaverse-1b10acfedc84
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/metaverse-taking-whole-industry-storm-gaurav-agarwaal/
https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology
https://www.wundermanthompson.com/insight/new-trend-report-into-the-metaverse